On this page, we have compiled a general guide for Grade 12 Geography Students who are doing their research on Tropical Cyclone Hagabis.
In exploring the characteristics and implications of Tropical Cyclone Hagibis, this research task explores various aspects of tropical cyclones, their development, impacts, and the mitigative strategies that can be employed to minimize their destructive effects. This analysis provides insightful understanding into the dynamics of such natural disasters, particularly focusing on Tropical Cyclone Hagibis.
Overview of Tropical Cyclone Hagabis:
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis, which struck Japan in October 2019, is remembered as one of the most potent and devastating cyclones to hit the region in recent decades. Rapidly intensifying to a Category 5 super typhoon, Hagibis showcased the catastrophic potential of tropical cyclones, with its development fueled by exceptionally warm ocean temperatures and the release of immense amounts of latent heat. Making landfall on the Izu Peninsula on October 12, the cyclone brought unprecedented rainfall, leading to widespread flooding, landslides, and significant infrastructural damage. Hagibis resulted in the loss of over 80 lives, highlighted the urgent need for effective disaster preparedness and response strategies, and became a focal point for discussions on climate change’s impact on the frequency and intensity of such natural disasters.
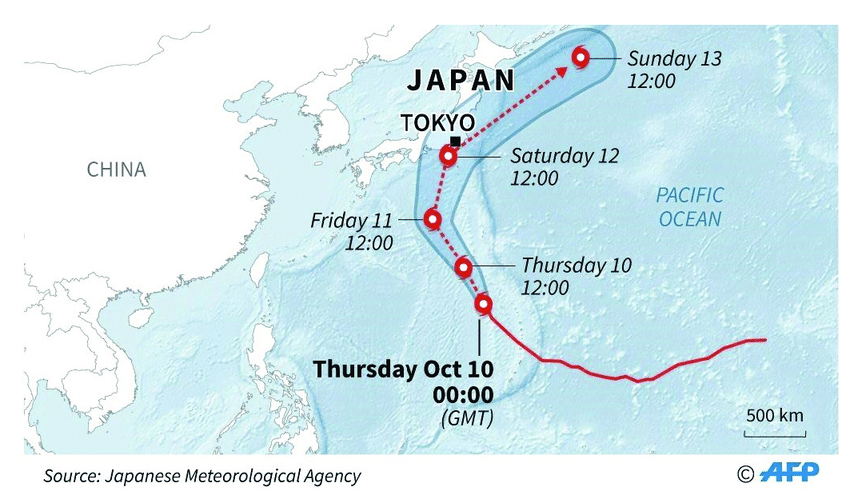
Map indicating the path of the tropical cyclone Hagabis
Map indicating the path of the tropical cyclone Hagabis:
Why do tropical cyclones develop in late summer?
Tropical cyclones predominantly develop in late summer due to the elevated sea temperatures that prevail during this period. The warm waters serve as the energy source that fuels the cyclones, facilitating the evaporation of warm, moist air that ascends, cools, and condenses to form storm systems. This process is essential for the genesis and intensification of tropical cyclones.
What is the impact of coriolis force and latent heat on the development of tropical cyclones?
The development of tropical cyclones is significantly influenced by the Coriolis force and the release of latent heat. The Coriolis force, a result of the Earth’s rotation, imparts a rotational motion to the storm, which is crucial for the cyclone’s development. Latent heat, released during the condensation of water vapor in the air, provides the energy that intensifies the storm, contributing to the tropical cyclone’s growth and power.
The stage of development of the Tropical Cyclone Hagibis
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis underwent rapid intensification, evolving from a tropical storm to a Category 5 super typhoon in an exceptionally short period. This stage of development highlights the cyclone’s explosive energy release, attributed to the immense amount of latent heat generated during the condensation process, showcasing the cyclone’s capacity for rapid growth and intensification.
Why can category 1 tropical cyclones be more destructive (damaging) than category 5 tropical cyclones?
Category 1 tropical cyclones can be more destructive than Category 5 cyclones due to several factors, including their speed, trajectory, and the specific areas they impact. A Category 1 cyclone, moving slowly over a densely populated area, can cause extensive damage through prolonged exposure to strong winds and heavy rainfall, leading to significant flooding and infrastructural damage.
How did Tropical Cyclone Hagibis impact the following?
Environment
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis had a profound impact on the environment, causing extensive flooding and landslides. The environmental degradation included overflowed rivers, soil erosion, and significant damage to natural habitats, disrupting the ecological balance in the affected areas.
Economy
The economic ramifications of Hagibis were severe, with widespread damage to infrastructure, residential areas, and the agricultural sector. The cyclone’s destruction led to substantial economic losses, highlighting the need for effective disaster preparedness and recovery strategies.
People/Communities
The impact on people and communities was devastating, with Hagibis causing fatalities, displacements, and extensive damage to homes and community facilities. The cyclone’s effects underscored the vulnerability of communities to such natural disasters and the importance of robust emergency response and support systems.
What precautions can be implemented/ or has been implemented to reduce the impact of Tropical Cyclone Hagibis?
The local government/Government of the country
The government’s response included issuing early evacuation orders, setting up emergency shelters, and investing in meteorological technology to improve storm predictions and responses. These measures were critical in minimizing the cyclone’s impact on affected communities.
The local residents
Local residents were encouraged to engage in preparedness activities, including assembling emergency kits, formulating evacuation plans, and identifying safe shelter locations. Community-level drills and infrastructure reinforcement also played vital roles in enhancing resilience to tropical cyclones.
Evaluating the impact of Global Warming on the frequency (regularity) of tropical cyclones.
Global warming, characterized by rising sea temperatures, is likely to increase the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones. The enhanced energy and moisture available in a warmer climate contribute to more potent and potentially more frequent tropical storms, raising the risk profile for regions prone to such natural phenomena.
Discussing the path of the tropical cyclone Hagabis
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis, notable for its rapid intensification and devastating impact, traced a path that left a significant imprint on Japan in October 2019. This section discusses the journey of Hagibis from its formation to its landfall and the aftermath.
Formation and Intensification
Originating from a tropical depression in the Western Pacific Ocean, Hagibis escalated into a super typhoon at an unprecedented rate. Key factors contributing to its rapid growth included exceptionally warm sea temperatures and favorable atmospheric conditions, propelling it to reach Category 5 status. This phase of Hagibis highlights the dynamic and powerful nature of tropical cyclones under conducive environmental conditions.
Movement Towards Japan
As it advanced towards Japan, Hagibis started to show signs of weakening but remained a robust and extensive storm system. The approach of Hagibis was closely monitored, with meteorologists predicting significant impacts due to its size and strength. The anticipation and preparedness for Hagibis underscore the importance of early warning systems in mitigating the effects of such natural disasters.
Landfall and Impact
Making landfall on the Izu Peninsula on October 12, Hagibis brought with it unprecedented rainfall, leading to widespread flooding, landslides, and considerable infrastructural damage. The severity of Hagibis at landfall demonstrated the destructive potential of tropical cyclones, especially in densely populated regions.
Aftermath
The aftermath of Hagibis was marked by a significant loss of life, with over 80 fatalities reported. The storm’s impact extended beyond immediate physical damage, affecting millions through displacement, power outages, and disrupted transportation networks. The recovery and rebuilding efforts in the wake of Hagibis underscored the resilience of the affected communities and the critical role of efficient disaster response and recovery strategies.
Conclusion/Summary
Tropical Cyclone Hagibis serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of tropical cyclones and the critical need for comprehensive understanding, preparedness, and mitigation strategies. While natural disasters cannot be entirely prevented, improved preparedness, efficient early warning systems, and community education can significantly mitigate their impacts. Furthermore, addressing global warming’s role in the increasing severity and frequency of tropical cyclones is imperative for safeguarding vulnerable communities in the future.
Subscribe to our email newsletter to get the latest posts delivered right to your email.


[…] Tropical cyclones Hagibis […]