Welcome to Grade 8 Technology, where we will delve into the exciting world of Mechanical Systems and Control. This course aims to provide students with an understanding of basic mechanical principles, the types of simple machines, and how control systems govern their operations. Through hands-on activities, theoretical exercises, and practical applications, students will gain knowledge and skills that lay a foundation for future studies in technology, engineering, and applied sciences.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
Understand Basic Mechanical Concepts
- Define what a machine is and describe how it can make work easier.
- Identify the six basic types of simple machines: levers, pulleys, wheels and axles, inclined planes, screws, and wedges.
Explore the Role of Levers
- Understand the three classes of levers and identify examples of each in everyday life.
- Explain the concept of a fulcrum and how its position can change the mechanical advantage of a lever.
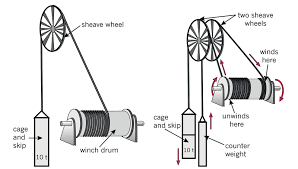
Grasp the Principles of Pulleys and Wheels
- Distinguish between fixed and movable pulleys and their applications.
- Describe how the wheel and axle function as a simple machine.
Study Gears and their Functionality
- Understand the basic types of gears, including spur gears, bevel gears, and worm gears.
- Explain how the arrangement and size of gears can influence speed, force, and direction in mechanical systems.
Understand Control Systems
- Describe the basic components of a control system, including inputs, processes, and outputs.
- Recognize the role of sensors, controllers, and actuators in a control system.
Explore the Conservation of Energy
- Understand the principle of conservation of energy as it applies to mechanical systems.
- Explain how energy is transferred and transformed in simple machines.
Investigate Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems
- Describe how hydraulic systems use liquids to transmit force and motion.
- Understand the basic principles behind pneumatic systems that use gases for similar purposes.
Apply Knowledge through Hands-On Activities
- Engage in experiments and projects that reinforce theoretical knowledge.
- Demonstrate the ability to solve practical problems using mechanical systems and control concepts.
By mastering these objectives, students will have a solid groundwork for understanding how mechanical systems and controls play a crucial role in modern technology and everyday life.
Below are some sample questions and answers related to Grade 8-level mechanical systems and controls. These are intended for educational purposes and can serve as a starting point for understanding basic mechanical concepts:
Technology Grade 8 Mechanical Systems and Control Questions and Answers
1. What is a simple machine?
2. Name the six types of simple machines.
3. What is the purpose of a lever?
4. What is the difference between a pulley and a wheel and axle?
5. How do gears work in a mechanical system?
6. What is a fulcrum in the context of a lever?
7. What is mechanical advantage?
8. What are input and output forces?
9. What is the principle of conservation of energy in mechanical systems?
10. How does a hydraulic system work?
Answers
1. What is a simple machine?
A simple machine is a basic mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. Simple machines make work easier but do not change the amount of work done.
2. Name the six types of simple machines.
The six types of simple machines are the lever, inclined plane, wheel and axle, screw, pulley, and wedge.
3. What is the purpose of a lever?
The purpose of a lever is to amplify an input force to provide a greater output force, which makes it easier to do work like lifting, moving, or cutting objects.
4. What is the difference between a pulley and a wheel and axle?
A pulley is used to change the direction of a force and can magnify force, but it usually involves a rope or cable. A wheel and axle consist of a wheel attached to a smaller axle so that these two parts rotate together, transferring force from one to the other.
5. How do gears work in a mechanical system?
Gears are used to transmit power from one part of a mechanical system to another. They can increase speed, change direction, or increase force depending on their size and the arrangement.
6. What is a fulcrum in the context of a lever?
A fulcrum is the pivot point around which a lever rotates. The position of the fulcrum, relative to the input and output forces, determines the mechanical advantage of the lever.
7. What is mechanical advantage?
Mechanical advantage is the factor by which a machine multiplies the force put into it. It is calculated as the output force divided by the input force.
8. What are input and output forces?
Input force is the force you apply to a machine, and output force is the force that the machine applies to do work.
9. What is the principle of conservation of energy in mechanical systems?
The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. In mechanical systems, the total energy remains constant, although it may change from kinetic to potential energy or vice versa.
10. How does a hydraulic system work?
In a hydraulic system, fluid is used to transmit pressure from one point to another. When force is applied to the fluid at one end, the same force is exerted at the other end, allowing for the amplification of force and motion.
Questions
11. What is torque?
12. How do inclined planes make work easier?
13. Describe the concept of “input” and “output” in a control system.
14. What is the difference between hydraulic and pneumatic systems?
15. How do screws function as simple machines?
16. What is a gear ratio, and why is it important?
17. Describe the basic concept of a linkage in mechanical systems.
18. What are actuators, and what role do they play in control systems?
19. How does a wedge function as a simple machine?
20. What are sensors, and how do they function in control systems?
Answers
11. What is torque?
Torque is the rotational force applied to an object. It is the product of the force applied and the distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied.
12. How do inclined planes make work easier?
Inclined planes make work easier by reducing the amount of force needed to lift an object to a certain height. Instead of lifting the object directly upward, it is moved along the inclined plane, requiring less force but over a longer distance.
13. Describe the concept of “input” and “output” in a control system.
In a control system, “input” refers to the information or signals fed into the system, often from sensors. “Output” is the action or response that the control system generates based on the input, typically performed by actuators.
14. What is the difference between hydraulic and pneumatic systems?
Hydraulic systems use liquids to transmit force and motion, while pneumatic systems use gases. Hydraulic systems are generally more suitable for applications requiring high force, while pneumatic systems are often used in applications requiring speed and flexibility.
15. How do screws function as simple machines?
Screws are essentially inclined planes wrapped around a cylinder. When the screw is turned, it converts rotational motion into linear motion, allowing objects to be lifted or fastened with less effort.
16. What is a gear ratio, and why is it important?
Gear ratio is the ratio between the number of teeth on the driving gear to the number of teeth on the driven gear. It is important because it determines the mechanical advantage, speed, and direction of force in gear systems.
17. Describe the basic concept of a linkage in mechanical systems.
A linkage is a set of connected rigid bodies that are arranged to transmit force or motion. They are used in various mechanical systems to change the direction, speed, or magnitude of force.
18. What are actuators, and what role do they play in control systems?
Actuators are devices that convert energy into motion or action. In a control system, actuators receive signals from a controller to perform specific actions, such as opening a valve or moving a lever.
19. How does a wedge function as a simple machine?
A wedge is used to separate two objects or portions of an object, or to hold an object in place. It converts the force applied to its blunt end into force exerted at its edges.
20. What are sensors, and how do they function in control systems?
Sensors are devices that detect changes in the environment, like temperature or light, and convert them into signals that can be read by a control system. They serve as the ‘eyes and ears’ of the control system, providing the input needed for the system to make decisions.