Human Reproduction Grade 12 Notes with Questions and Answers:
The Grade 12 Life Sciences curriculum in South Africa includes a section on Human Reproduction. The main topics covered in this section include:
- Male Reproductive System: This topic covers the anatomy and physiology of the male reproductive system, including the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and urethra. It also covers the process of spermatogenesis, as well as the production and regulation of male hormones.
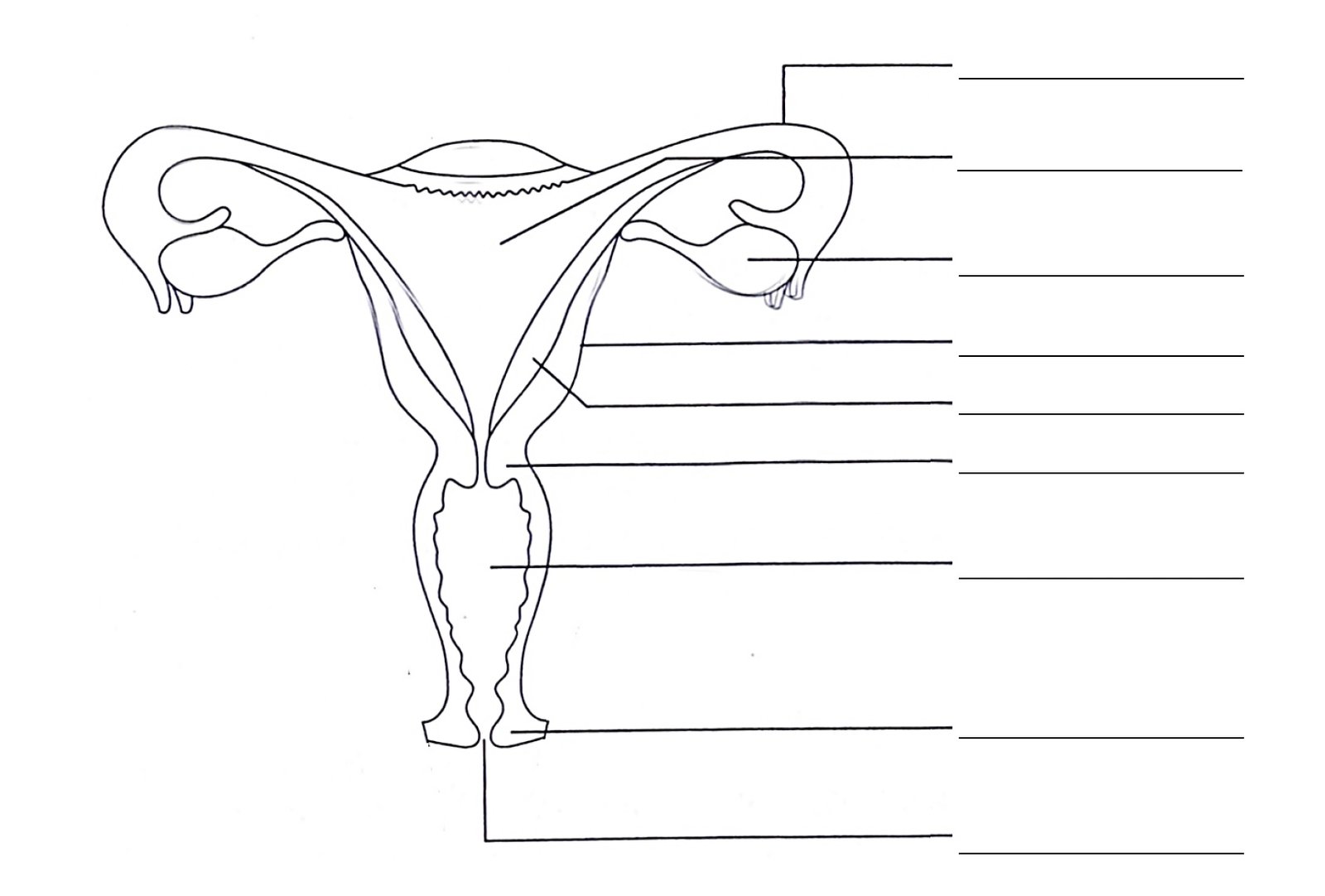
- Female Reproductive System: This topic covers the anatomy and physiology of the female reproductive system, including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. It also covers the process of oogenesis, as well as the production and regulation of female hormones.
- Fertilization and Implantation: This topic covers the process of fertilization, including the roles of sperm and egg, and the events that occur during fertilization. It also covers the process of implantation, including the development of the zygote and its attachment to the uterine wall.
- Embryonic and Fetal Development: This topic covers the stages of embryonic and fetal development, including the formation of the placenta, the development of the major organ systems, and the changes that occur throughout pregnancy.
- Pregnancy and Childbirth: This topic covers the stages of labor and delivery, as well as the physiological changes that occur during pregnancy and childbirth. It also covers the factors that can influence the health of the mother and baby during pregnancy and delivery.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections: This topic covers the transmission, symptoms, and treatment of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), as well as the importance of practicing safe sex to prevent STIs.
Video Lesson: Human Reproduction Grade 12 Life Sciences
By studying these topics, Grade 12 Life Sciences students will gain a deep understanding of human reproduction, and the processes that lead to the creation and development of a new human life. They will also gain important information about reproductive health and safety, which will help them to make informed decisions about their own health and well-being.
Human Reproduction Grade 12 Notes Download
Exam Questions and Answers: Human Reproduction Grade 12 Life Sciences
Here are some sample questions and answers on Human Reproduction for Grade 12 Life Sciences in South Africa:
- What are the main organs of the male reproductive system and what is their function?
Answer: The main organs of the male reproductive system are the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and urethra. Their functions include the production and storage of sperm, the transport of sperm from the testes to the urethra, and the production and secretion of seminal fluid, which helps to nourish and protect the sperm.
- What is the difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis?
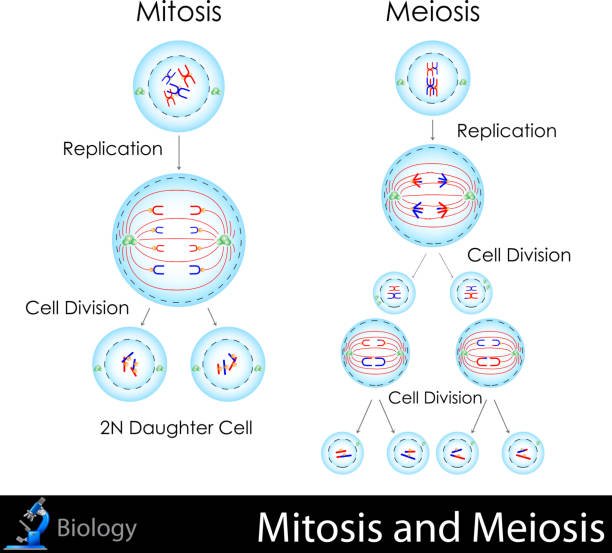
Answer: Spermatogenesis is the process of sperm cell production in males, while oogenesis is the process of egg cell production in females. The main difference between the two processes is that spermatogenesis produces four sperm cells from one parent cell, while oogenesis produces one egg cell and three polar bodies from one parent cell.
- What are the stages of embryonic development and what occurs during each stage?
Answer: The stages of embryonic development include the zygote, blastocyst, gastrula, and neurula stages. During the zygote stage, the fertilized egg undergoes cell division to form a ball of cells. During the blastocyst stage, the embryo implants in the uterus and the cells begin to differentiate into different cell types. During the gastrula stage, the three germ layers form, which will give rise to different tissues and organs. During the neurula stage, the neural tube forms, which will eventually develop into the brain and spinal cord.
- What is the role of the placenta during pregnancy?
Answer: The placenta is an organ that develops during pregnancy and serves as the interface between the mother and fetus. It provides oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus, removes waste products, and secretes hormones that help to maintain the pregnancy. The placenta also acts as a barrier, preventing harmful substances from passing from the mother to the fetus.
- What are some common sexually transmitted infections and how can they be prevented?
Answer: Common sexually transmitted infections include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, human papillomavirus (HPV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These infections can be prevented by practicing safe sex, which includes using condoms and getting tested regularly for STIs. It is also important to be informed about the risks and symptoms of STIs, and to seek medical treatment if you suspect that you may have an infection.
- What is the role of hormones in the female reproductive system?
Answer: Hormones play a key role in regulating the female reproductive system. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland secrete hormones that stimulate the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone. These hormones control the menstrual cycle and are responsible for the development of female secondary sex characteristics, as well as the growth and development of the uterus and other reproductive organs.
- What is the process of fertilization and implantation in humans?
Answer: Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell penetrates and fertilizes an egg cell, creating a zygote. The zygote then begins to divide and move down the fallopian tube towards the uterus, where it implants in the uterine wall. Implantation occurs when the blastocyst attaches to the uterine lining, and the placenta begins to develop.
- What are some common causes of infertility in men and women?
Answer: Infertility in men can be caused by a low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or structural abnormalities in the reproductive system. Infertility in women can be caused by hormonal imbalances, ovulation disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, or structural abnormalities in the reproductive system. Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, alcohol use, and obesity, can also contribute to infertility in both men and women.
- What are some of the risks associated with pregnancy and childbirth?
Answer: Pregnancy and childbirth can carry certain risks, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, preterm labor, and postpartum hemorrhage. Complications during childbirth can also arise, such as fetal distress, shoulder dystocia, or complications from a C-section. It is important for pregnant women to receive regular prenatal care and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider.
- What is the importance of family planning and contraception?
Answer: Family planning and contraception are important for ensuring that individuals and couples can plan and space their pregnancies, and make informed decisions about their reproductive health. Contraception can help to prevent unintended pregnancies, reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections, and improve maternal and child health outcomes. It is important to have access to a range of effective and affordable contraceptive options, as well as education about how to use them correctly.