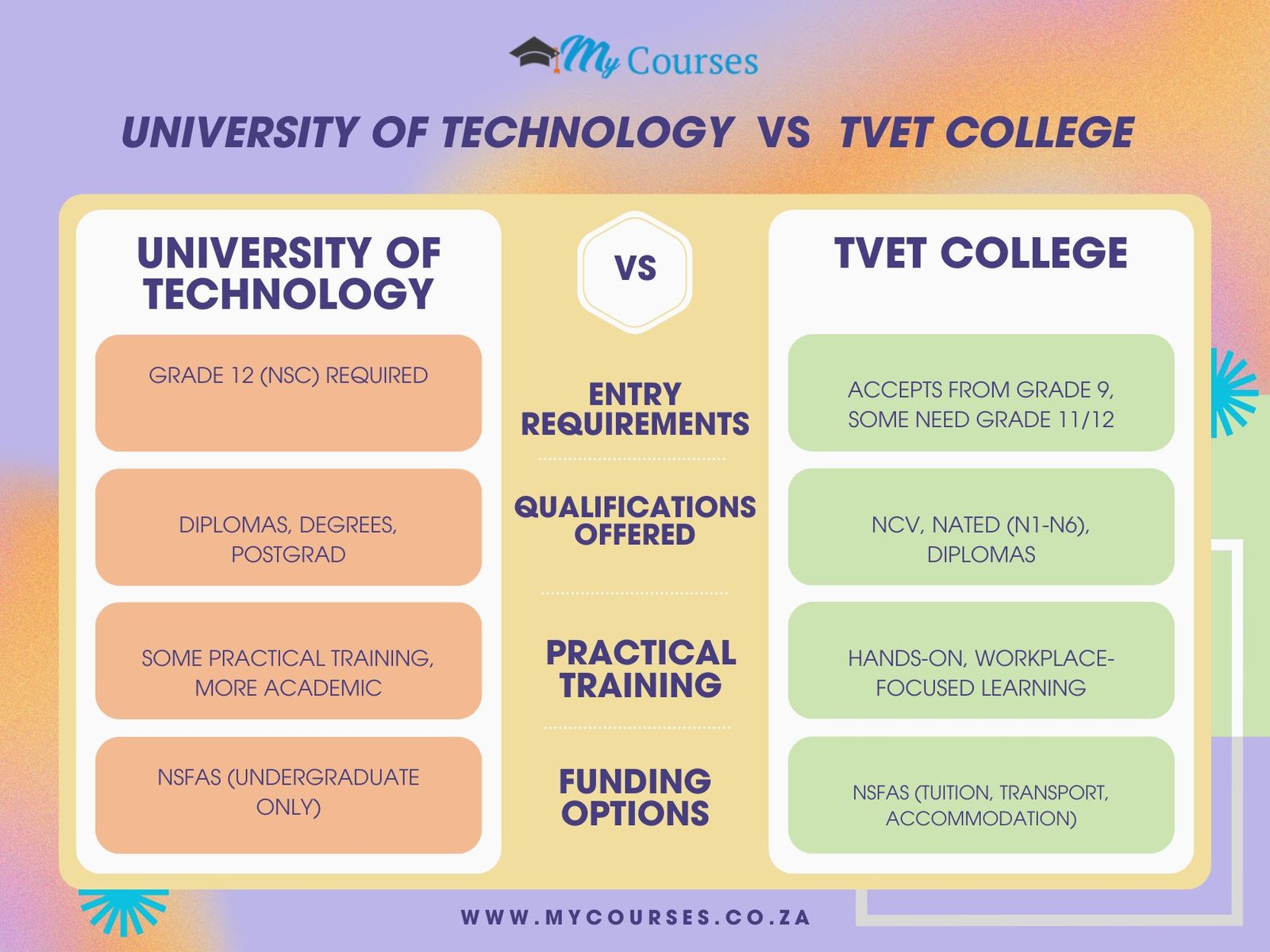
On this page, we draw a table to differentiate between University of Technology and a TVET college. Remember, this is coming from Lindiwe’s case study, right?
In order to draw a table that differentiates between a University of Technology and a TVET College, you need to remember Life Orientation Grade 11 Chapter 3: Careers and Career Choices Term 1 work.
We will differentiate between University of Technology and TVET College based on:
- Entry requirements – A University of Technology requires Grade 12, as well as specific subject marks and APS score, whereas TVET colleges accept students with just a Grade 9 achievement.
- Qualifications offered – Universities of Technology can offer National Diplomas, Bachelor’s Degrees, Honours, Masters, up to Doctorates, while TVET colleges only offer National Certificates and National Diplomas.
- Practical vs Academic Work – Universities of Technology offer a mix of practical and academic work, whereas TVET colleges strictly offer courses focused on practical skills.
- Funding – Both Universities of Technology and TVET colleges are funded by NSFAS.
Below is a table to differentiate between University of Technology and a TVET college:
| Aspect | University of Technology | TVET College |
|---|---|---|
| Entry Requirements | Requires Grade 12 (NSC) with specific subject requirements | Accepts learners from Grade 9, but some courses require Grade 11 or 12 |
| Qualifications Offered | Offers National Diplomas, Bachelor’s Degrees, Honours, Masters, and Doctorates | Offers National Certificates (Vocational) (NCV), NATED (N1-N6), and Diplomas |
| Practical Training | Includes practical training, but with more academic coursework | Strong focus on practical skills, workplace simulation, and industry-linked learning |
| Funding Options | NSFAS-funded for eligible undergraduate students | NSFAS-funded for eligible students, covering tuition, transport, and accommodation |

Lindiwe’s Case Study