Discussing one way in which Global Warming Aggravates the Effect of Radiation:
How Global Warming Works
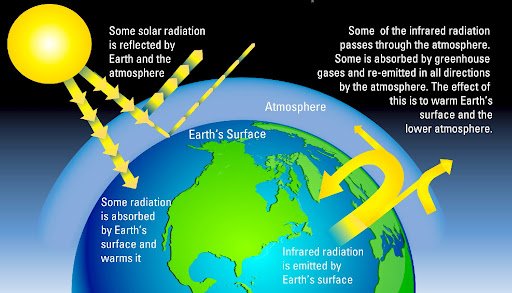
Certain gases in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases — specifically, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, tropospheric ozone, and CFCs — because they allow shortwave radiation from the sun to pass through the atmosphere and warm the Earth’s surface. The energy that then radiates out from the surface, longwave radiation, is trapped by the same greenhouse gases, warming the air, oceans, and land. This process, appropriately dubbed “the greenhouse effect,” is how global warming occurs. Black carbon, a particle rather than a gas, also has a very large warming impact.
ANSWER: So, one way in which Global Warming Aggravates the Effect of Radiation is through the greenhouse effect
How the greenhouse effect works
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet’s atmosphere warms the planet’s surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere. Radiatively active gases in a planet’s atmosphere radiate energy in all directions.
Climate change occurs as a result of an imbalance between incoming and outgoing radiation in the atmosphere. The global mean temperatures may increase up to 5.4°C by 2100.
Search Geography Grade 12 Study Resources
Looking for something in particular?
Search and find some of the useful resources for Grade 12 Geography including: Past Papers, Exercises, Class Assessments Plans, Assignments and Answers, Research Tasks, Essays Topics and more. Resources are for all terms: Term 1, Term 2, Term 3, and Term 4.
Sources
https://www.biologicaldiversity.org/programs/climate_law_institute/global_warming_what_how_why/
https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/74077