On this page, we discuss the six care and treatment of a patient with dermatitis:
Dermatitis refers to inflammation of the skin, and it can manifest in various forms such as eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, or contact dermatitis. Symptoms typically include itching, redness, and swelling. Managing dermatitis often requires a comprehensive approach to alleviate discomfort and address the underlying causes. In South Africa, as in many parts of the world, the care and treatment of a patient with dermatitis is essential for improving the quality of life. This article discusses six crucial aspects of care and treatment for a person suffering from dermatitis.
Six Care and Treatment of a Patient with Dermatitis
Six Care and Treatment of a Patient with Dermatitis are:
- Diagnosis and Understanding the Cause
- Emollient Therapy
- Topical Medications
- Avoidance of Triggers
- Education and Support
- Monitoring and Follow-up Care
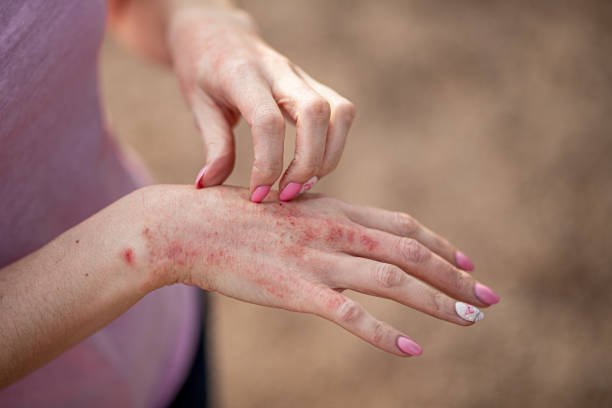


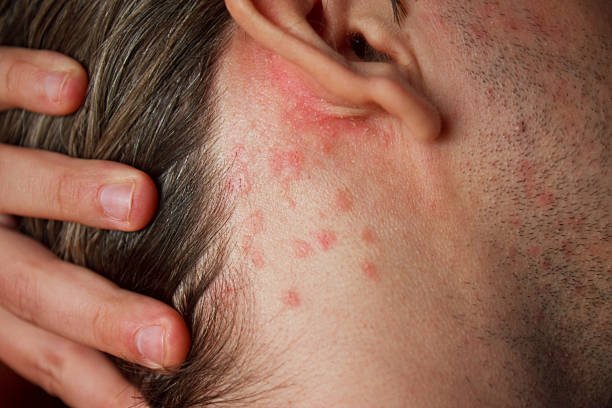

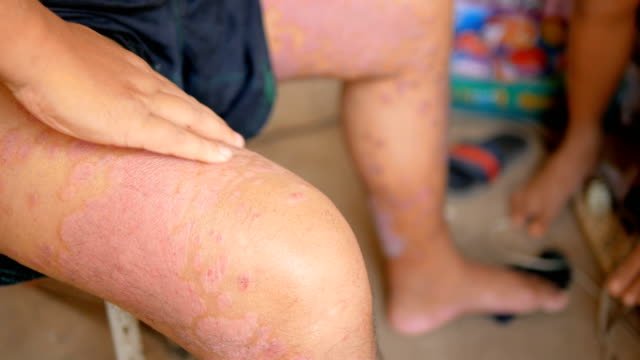
1. Diagnosis and Understanding the Cause
Introduction to Diagnosis
A proper diagnosis is the first step in the effective management of dermatitis. By understanding the specific type of dermatitis and its triggers, treatment can be tailored to the patient’s needs.
Methods of Diagnosis
A healthcare provider may use a physical examination, medical history, patch testing, or other diagnostic tools to determine the type and cause of dermatitis.
2. Emollient Therapy
Introduction to Emollient Therapy
Emollients are moisturising treatments applied directly to the skin to soothe and hydrate.
Importance of Emollient Therapy
Emollients help in maintaining the skin’s barrier function, reducing dryness, and relieving itchiness.
3. Topical Medications
Introduction to Topical Medications
Topical medications, such as corticosteroids, can be prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Application of Topical Medications
These are typically applied as creams or ointments to the affected areas, following the healthcare provider’s instructions.
4. Avoidance of Triggers
Introduction to Trigger Avoidance
Understanding and avoiding triggers can prevent flare-ups and reduce the severity of symptoms.
Examples of Triggers
Triggers may include allergens, irritants, certain foods, or environmental factors.
5. Education and Support
Introduction to Education and Support
Providing the patient with education about their condition and ongoing support is key to managing dermatitis effectively.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers can teach patients about skin care routines, medication management, and strategies to avoid triggers.
6. Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Introduction to Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up care with healthcare providers ensure that the treatment plan is working and can be adjusted if necessary.
Ongoing Assessments
This may include regular assessments of the skin’s condition, reviewing medications, and adjusting treatment as needed.
Conclusion: Comprehensive Approach to Dermatitis Care
Dermatitis is a complex skin condition that requires a multifaceted approach to care and treatment. Through proper diagnosis, utilization of emollients, prescription of topical medications, avoidance of triggers, patient education, and regular monitoring, individuals with dermatitis can experience relief and improved quality of life.
Whether you’re a high school learner in South Africa looking to understand medical care or someone dealing with dermatitis, understanding these six aspects provides insight into how this condition can be managed effectively. Treatment is often personalized, reflecting the unique needs and circumstances of each patient. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with dermatitis can navigate their condition with confidence and support.

